Verifying Proxy Contracts
This guide will walk you through proxy contract verification using @tenderly/hardhat-tenderly.
Considerations
- Automatic verification of proxy contracts is possubile out of the box with
@tenderly/hardhat-tenderlyplugin at versions- 1.x.y >= 1.10.0
- 2.x.z >= 2.1.0
- If you’re at a lower version, we recommend upgrading.
- Without updating the library, you must apply the workaround to enable automatic proxy verification.
- Automatic verification of proxy contracts is possible only when using
hardhat-upgrades. - Automatic verification of proxy contracts not possible with hardhat-ignition.
Upgrading
For automatic verification update @tenderly/hardhat-tenderly to >= 1.10.0 or >= 2.1.0.
npm update @tenderly/hardhat-tenderlyAutomatic verification
When using Hardhat that relies on @tenderly/hardhat-tenderly at versions >=1.10.0 and >=2.1.0, automatic verification is supported.
This version of the library supports automatic and manual verification of three types of proxies:
TransparentUpgradeableProxyUUPSUpgradeableProxyBeaconProxy
Enable TENDERLY_AUTOMATIC_POPULATE_HARDHAT_VERIFY_CONFIG env variable
When verifying proxies, the Tenderly-Hardhat plugin uses @nomicfoundation/hardhat-verify with the @openzepellin/hardhat-upgrades extension beneath.
@nomicfoundation/hardhat-verify needs to be configured to include the verification URL.
By setting TENDERLY_AUTOMATIC_POPULATE_HARDHAT_VERIFY_CONFIG to true in your .env file, you’re allowing the Tenderly-Hardhat plugin to automatically populate the configuration for you.
Write deployment script
For a clearer view, you can check out this GitHub repo and go to scripts/proxy/ to see the full example.
Deploy the proxy as usual using deployProxy from the @openzeppelin/hardhat-upgrades extension.
You must capture the object returned by the waitForDeployment function to interact with it further.
Under the hood, the automatic verification is implemented by wrapping the deployProxy, and waiting for completion of the deployment.
import { ethers, upgrades } from "hardhat";
async function main() {
console.log(
"🖖🏽[ethers] Deploying TransparentUpgradeableProxy with VotingLogic as implementation on Tenderly.",
);
const VotingLogic = await ethers.getContractFactory("VotingLogic");
let proxyContract = await upgrades.deployProxy(VotingLogic);
proxyContract = await proxyContract.waitForDeployment();
const proxyAddress = await proxyContract.getAddress();
console.log("VotingLogic proxy deployed to:", proxyAddress);
console.log(
"VotingLogic impl deployed to:",
await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
);
}
main().catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
process.exitCode = 1;
});Run the script
TENDERLY_AUTOMATIC_VERIFICATION=true \
TENDERLY_AUTOMATIC_POPULATE_HARDHAT_VERIFY_CONFIG=true \
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.tsWorkaround for lower versions
When using @tenderly/hardhat-tenderly at versions < 1.10.0 and < 2.1.0, this workaround will enable automatic verification.
You need to verify the following:
- The proxy contract (e.g. OpenZeppelin’s proxies)
- Implementation behind the proxy
- Any dependencies the implementation has
- New implementation instances deployed with upgrades
The verification process varies depending on the proxy contract type and the implementation.
Overview
In this guide, we’ll use an example Hardhat project and the @tenderly/tenderly-hardhat plugin to demonstrate the verification of OpenZeppelin’s UUPSUpgradeable, TransparentUpgradeableProxy, and BeaconProxy alternatives.
Proxy contracts need to be verified manually. Turn off automatic verification like so:
import * as tenderly from '@tenderly/hardhat-tenderly';
// use manual verification
tenderly.setup({ automaticVerifications: false });To obtain the address of the deployed implementation, use the @openzeppelin/upgrades-core package and getImplementationAddress function.
Verifying the proxy implementation is usually straightforward; verify it just like any other contract.
await tenderly.verify({
// the new implementation contract
name: 'VaultV2',
// the address where implementation is deployed
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, await proxy.getAddress()),
});To verify the proxy instance, you need to complete these two preliminary steps:
- Load the exact smart contract of the proxy depending on the type of proxy you’re using, so it gets compiled. You’ll need to import the proxy contracts through the compiler by creating a dummy .sol file.
- Modify
hardhat.config.tsto specify the settings OpenZepplin contracts were compiled with.
Once these steps are completed, you can proceed to verify the proxy just as you would any other contract.
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'ERC1967Proxy', // or TransparentUpgradeableProxy or BeaconProxy
address: await proxy.getAddress(),
});This video shows how to verify proxy contracts with Hardhat and Tenderly:
Cloning the example repo
Clone the repo and install dependencies.
git clone git@github.com:Tenderly/tenderly-examples.git
cd contract-verifications
npm iSetting up Tenderly CLI
Set up the Tenderly CLI.
brew tap tenderly/tenderly && brew install tenderly
tenderly loginConfiguring hardhat
Modify your hardhat.config.ts file and update the tenderly.username and tenderly.project with your Tenderly username and project slugs.
Use DevNets
Migrate to Virtual TestNets
For new projects, we recommend starting with TestNets.
For automatic migration of DevNets to TestNets, .
The fastest way to deploy and verify contracts is to use Tenderly DevNets.
Log into the Tenderly Dashboard and create a new DevNet template.
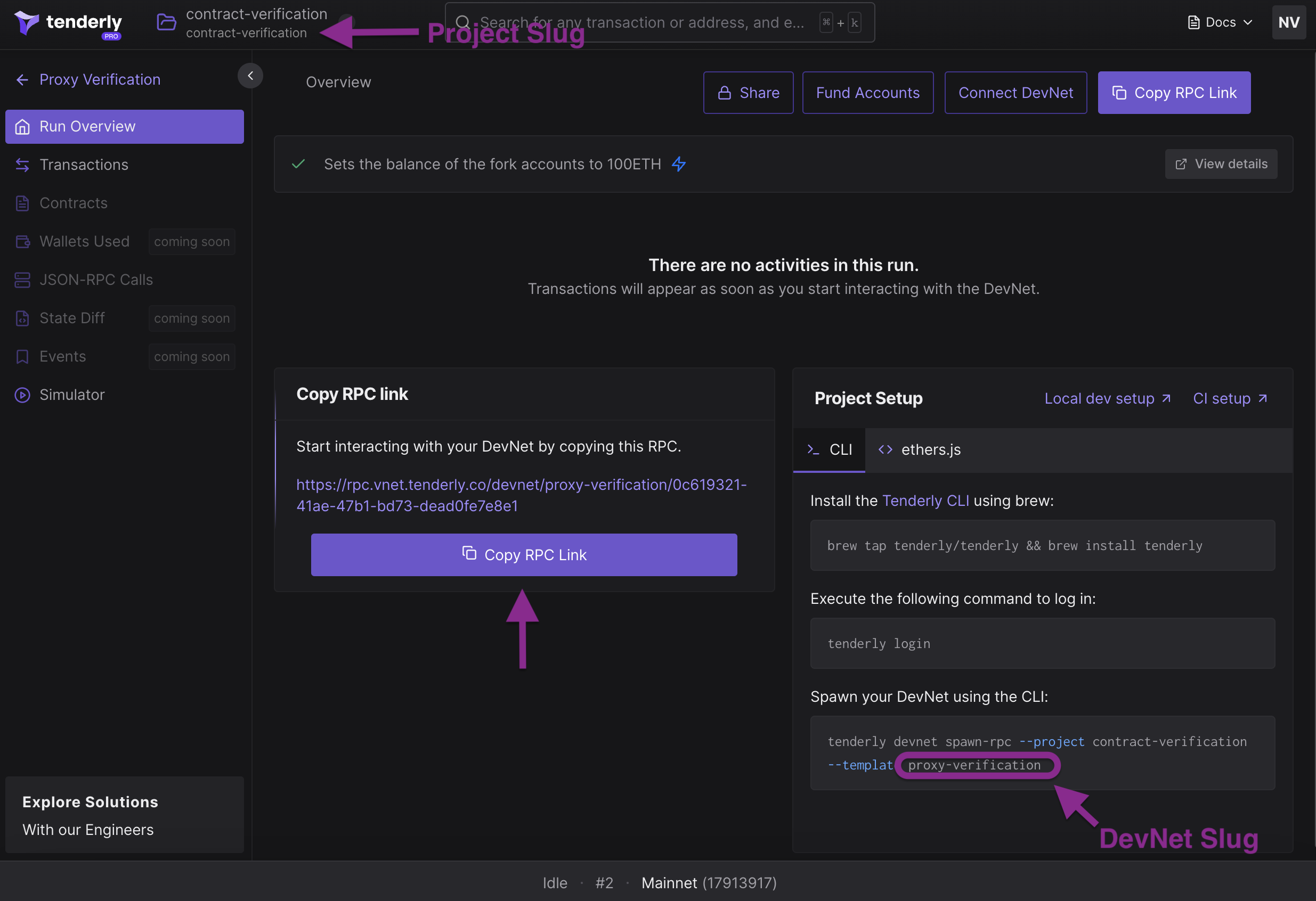
Project and DevNet slug
Spawn a DevNet
Spawn a DevNet from the template you created and use the generated RPC URL. You can spawn a DevNet and obtain the RPC in three ways:
- Click “Spawn DevNet” from the Dashboard and add the RPC link to
networks.tenderly.urlin thehardhat.config.tsfile. - Run the DevNet spawning command you copied from the Dashboard and paste the RPC link to
networks.tenderly.urlinhardhat.config.tsfile. - Run the
spawn-devnet-to-hardhatscript from the example project, which will spin up a fresh DevNet and update your Hardhat project automatically. ReplaceTENDERLY_PROJECT_SLUGandDEVNET_TEMPLATE_SLUGwith appropriate values. (see the screenshot)
npm run spawn-devnet-to-hardhat <TENDERLY_PROJECT_SLUG> <DEVNET_TEMPLATE_SLUG>Run the tests
Finally, run the tests.
.openzeppelin folder, that caches information about proxies and their implementations.rm -rf .openzeppelin && npx hardhat test --network tenderlyLoad the proxy contracts
To verify the proxy contract, create a DummyProxy.sol file and import the OpenZepplin proxy contracts you’re working with. In doing so, these contracts are loaded and have passed through the compiler, enabling you to reference the exact contract source of the proxy during verification.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/ERC1967/ERC1967Proxy.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/beacon/UpgradeableBeacon.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/beacon/BeaconProxy.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/transparent/TransparentUpgradeableProxy.sol";
abstract contract ERC1967ProxyAccess is ERC1967Proxy {}
abstract contract UpgradableBeaconAccess is UpgradeableBeacon {}
abstract contract BeaconProxyAccess is BeaconProxy {}
abstract contract TransparentUpgradeableProxyAccess is TransparentUpgradeableProxy {}Configure Solidity compiler overrides
The following overrides map was derived for @openzeppelin/contracts-upgradeable version 4.9.1.
They may differ for other versions of the package.
After compiling Openzepplin’s proxy contracts, you also need to specify the following:
- Version of the Solidity compiler that was used to compile the contracts
- Optimization settings used by Openzepplin’s upgrades plugin when performing proxy deployment/upgrades
The hardhat-tenderly plugin uses both the source code of smart contracts and compiler settings
for verification. If either of these settings is incorrect, the verification will fail.
Add the following overrides map to the config.solidity section of your Hardhat User config object.
const config: HardhatUserConfig = {
solidity: {
compilers: [{ version: '0.8.18' } /* OTHER COMPILER VERSIONS*/],
overrides: {
'@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/ERC1967/ERC1967Proxy.sol': {
version: '0.8.9',
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
'@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/transparent/TransparentUpgradeableProxy.sol': {
version: '0.8.9',
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
'@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/beacon/UpgradeableBeacon.sol': {
version: '0.8.9',
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
'@openzeppelin/contracts/proxy/beacon/BeaconProxy.sol': {
version: '0.8.9',
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
'contracts/proxy.sol': {
version: '0.8.9',
settings: {
optimizer: {
enabled: true,
runs: 200,
},
},
},
},
},
/* OTHER CONFIG */
};Example: Proxied Vault
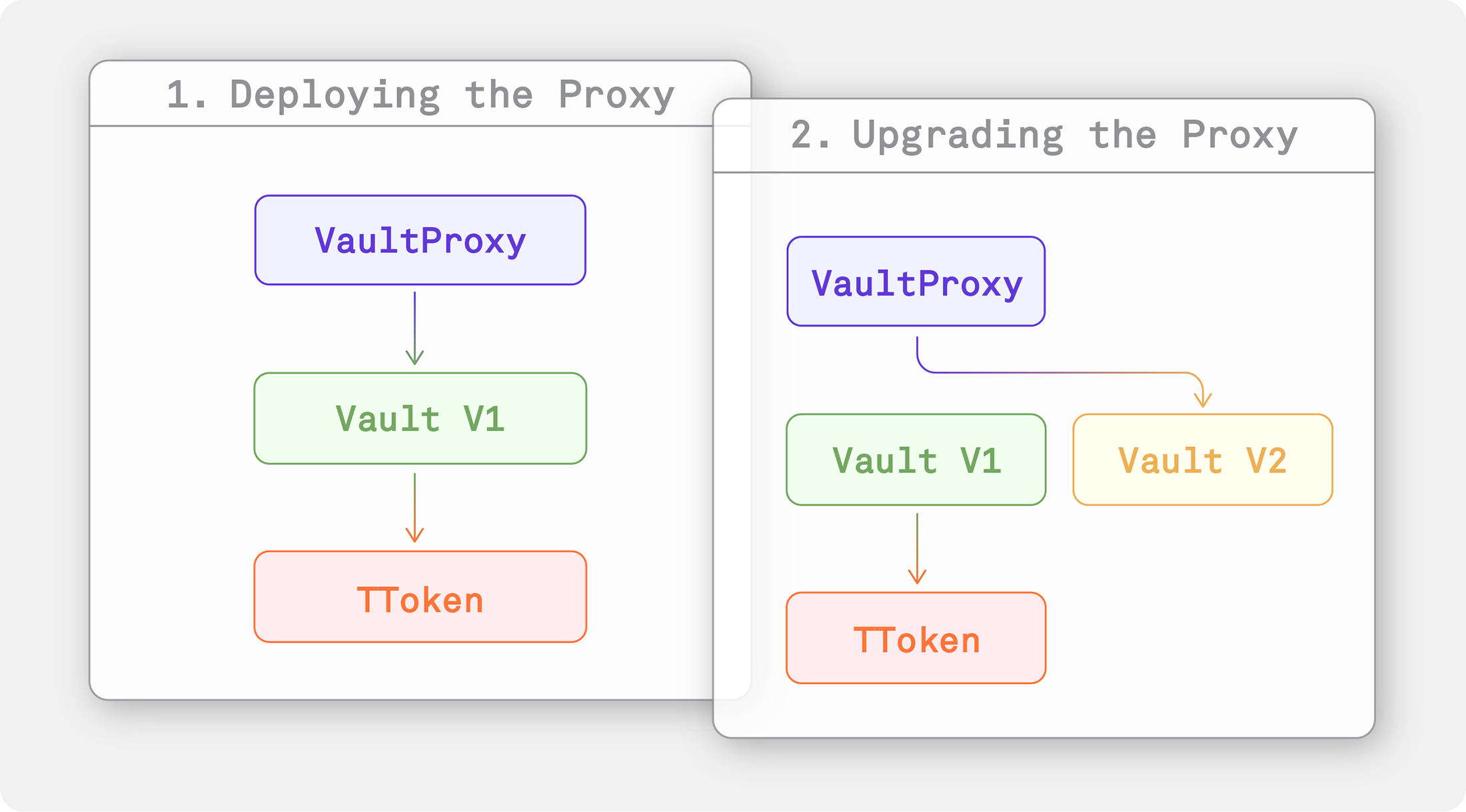
Below are code samples showing the verification of a proxied Vault contract. The Vault references an ERC-20 token (TToken). We’ll demonstrate how to verify both the implementation and the proxy using OpenZeppelin’s UUPS, Transparent, and Beacon proxying methods.
Verify a UUPS proxy
To verify the UUPS proxy and the underlying information, call the hardhat-tenderly plugin twice:
- To verify the implementation, you need to provide the following:
nameof your proxied contract (in our caseVault)- Address where the contract was deployed using the
getImplementationAddressmethod from@openzeppelin/upgrades-core.
- To verify the proxy, provide the following:
ERC1967Proxyas the proxy contractname- Address of the proxy
proxy.address
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, await proxy.getAddress()),
},
{
name: 'ERC1967Proxy',
address: await proxy.getAddress(),
},
);Complete Code Sample
Here’s a complete Hardhat test that does the following:
- Deploys the
TToken(needed for the vault) - Deploys
Vaultas a proxy, initialized with theTTokencontract - Verifies the proxy (
ERC1967Proxy) instance deployed atawait proxy.getAddress() - Verifies the implementation instance
Vault, deployed atgetImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, await proxy.getAddress()) - Upgrades the proxy to
VaultV2
import { getImplementationAddress } from '@openzeppelin/upgrades-core';
import { ethers, tenderly, upgrades } from 'hardhat';
import { Vault } from '../typechain-types';
describe('Vault', () => {
it('uups proxy deployment and verification', async () => {
const VaultFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('Vault');
const TokenFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('TToken');
let token = await ethers.deployContract('TToken');
token = await token.waitForDeployment();
const tokenAddress = await token.getAddress();
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'TToken',
address: tokenAddress,
});
let proxy = await upgrades.deployProxy(VaultFactory, [tokenAddress], {
kind: 'uups',
});
await proxy.waitForDeployment();
const proxyAddress = await proxy.getAddress();
console.log('Deployed UUPS ', {
proxy: proxyAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
},
{
name: 'ERC1967Proxy',
address: proxyAddress,
},
);
// upgrade
const vaultV2Factory = await ethers.getContractFactory('VaultV2');
proxy = (await upgrades.upgradeProxy(proxy, vaultV2Factory, {
kind: 'uups',
})) as Vault;
await proxy.waitForDeployment();
console.log('Upgraded UUPS ', {
proxy: proxyAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'VaultV2',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
});
});Verifying a TransparentUpgradable Proxy
To verify the UUPS proxy and the underlying information, call hardhat-tenderly while passing two contracts: Vault for the implementation, and TransparentUpgradeableProxy for the proxy itself.
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, await proxy.getAddress()),
},
{
name: 'TransparentUpgradeableProxy',
address: await proxy.getAddress(),
},
);- To verify the implementation, provide the following:
nameof your proxied contract (in our caseVault)- Address where the contract was deployed, using the
getImplementationAddressmethod from@openzeppelin/upgrades-core.
- To verify the proxy, provide the following:
TransparentUpgradeableProxyas the proxy contractname- Address of the proxy
await proxy.getAddress()
Complete Code Sample
import { getImplementationAddress } from '@openzeppelin/upgrades-core';
import { ethers, tenderly, upgrades } from 'hardhat';
import { Vault } from '../typechain-types';
describe('Vault', () => {
it('transparent upgradable proxy deployment and verification', async () => {
const VaultFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('Vault');
const TokenFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('TToken');
let token = await ethers.deployContract('TToken');
token = await token.waitForDeployment();
const tokenAddress = await token.getAddress();
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'TToken',
address: tokenAddress,
});
let proxy = await upgrades.deployProxy(VaultFactory, [tokenAddress], {
kind: 'transparent',
});
await proxy.waitForDeployment();
const proxyAddress = await proxy.getAddress();
console.log('Deployed transparent', {
proxy: proxyAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
},
{
name: 'TransparentUpgradeableProxy',
address: proxyAddress,
},
);
// upgrade
const vaultV2Factory = await ethers.getContractFactory('VaultV2');
proxy = (await upgrades.upgradeProxy(proxy, vaultV2Factory, {
kind: 'transparent',
})) as Vault;
await proxy.waitForDeployment();
console.log('Upgraded transparent ', {
proxy: proxyAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'VaultV2',
address: await getImplementationAddress(ethers.provider, proxyAddress),
});
});
});Verifying a Beacon Proxy
To verify the Beacon proxy and the underlying information, you have to verify two contracts: the Vault (implementation) and OpenZepplin’s UpgradableBeacon:
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddressFromBeacon(ethers.provider, await beacon.getAddress()),
},
{
name: 'UpgradeableBeacon',
address: await beacon.getAddress(),
},
);Complete Code Sample
import { getImplementationAddressFromBeacon } from '@openzeppelin/upgrades-core';
import { ethers, tenderly, upgrades } from 'hardhat';
import { BeaconProxy, UpgradeableBeacon } from '../typechain-types';
describe('Vault', () => {
it('beacon proxy deployment and verification', async () => {
const VaultFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('Vault');
const TokenFactory = await ethers.getContractFactory('TToken');
let token = await ethers.deployContract('TToken');
token = await token.waitForDeployment();
const tokenAddress = await token.getAddress();
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'TToken',
address: tokenAddress,
});
let beacon = (await upgrades.deployBeacon(VaultFactory)) as UpgradeableBeacon;
await beacon.waitForDeployment();
const beaconAddress = await beacon.getAddress();
let vault = await upgrades.deployBeaconProxy(beacon, VaultFactory, [tokenAddress], {
initializer: 'initialize',
});
await vault.waitForDeployment();
console.log('Deployed beacon ', {
proxy: beaconAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddressFromBeacon(ethers.provider, beaconAddress),
beacon: beaconAddress,
});
await tenderly.verify(
{
name: 'Vault',
address: await getImplementationAddressFromBeacon(ethers.provider, beaconAddress),
},
{
name: 'UpgradeableBeacon',
address: beaconAddress,
},
);
const vaultV2Factory = await ethers.getContractFactory('VaultV2');
// upgrade
vault = await upgrades.deployBeaconProxy(beacon, vaultV2Factory, [tokenAddress]);
await upgrades.upgradeBeacon(beaconAddress, vaultV2Factory, {});
console.log('Upgraded beacon ', {
proxy: beaconAddress,
implementation: await getImplementationAddressFromBeacon(ethers.provider, beaconAddress),
beacon: beaconAddress,
});
await tenderly.verify({
name: 'VaultV2',
address: await getImplementationAddressFromBeacon(ethers.provider, beaconAddress),
});
});
});